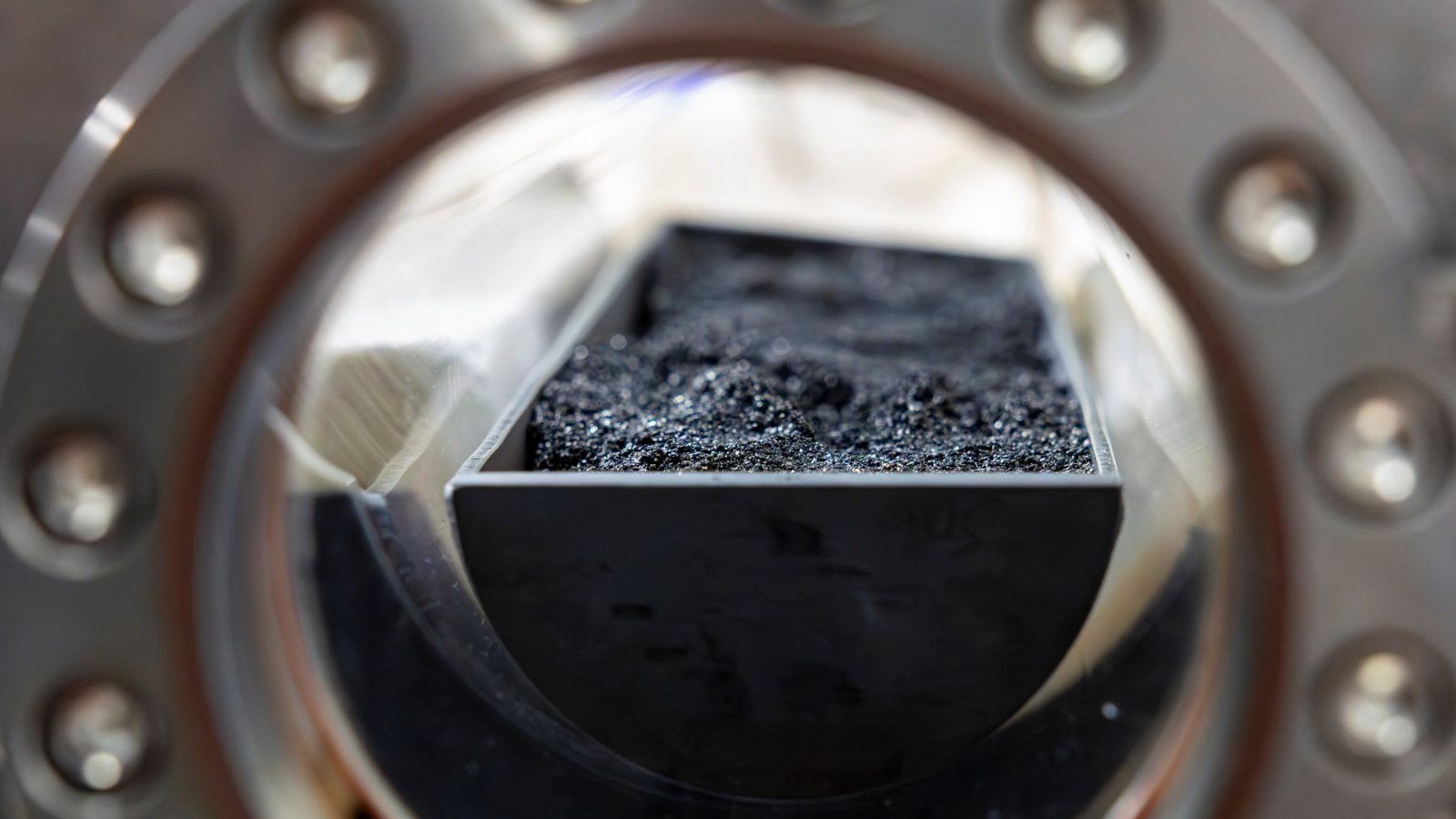
Researchers from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory have figured out a way to change the dirtiest fuel out there, coal, into materials to help build batteries for new clean vehicles.
The new process turns coal into graphite, which is an important component in electric car batteries. Graphite is used in the anode, which is the negatively charged end of the battery.
While we hear a lot about various other battery materials, such as lithium and cobalt, those materials actually occur in relatively lower quantities in electric car batteries.
The most common material in these batteries is actually graphite (see an infographic here, though this is for NMC-type batteries), so it’s important to ensure that there is a large supply of this material anywhere batteries need to be built.
And one of those places is in the US – thanks to President Joe Biden’s EV policies, there have been hundreds of billions in investment and hundreds of thousands of jobs brought to American manufacturing, largely in the form of battery plants to ensure that vehicles with modern technology will be made right here in America. Those policies also focused on ensuring onshored or “friend-shored” critical mineral supply for battery materials, such as graphite.
But there’s a problem: a majority of the world’s graphite comes from China. While this isn’t necessarily a problem in and of itself, it’s always better to have multiple sources for any particular material, so that one entity can’t throw their weight around if they see an opportunity. And given the anti-China saber-rattling that a certain treasonous reality TV host regularly engages in, it’s entirely possible that global tensions could result in disruption of graphite supply chains, which could then jeopardize the aforementioned burgeoning US EV manufacturing industry (which that same reality TV host/convicted felon seems determined to ensure does not flourish).
So, in come researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratories, who figured out a way to turn something that America still has a lot of – coal – into graphite.
It’s not too big of a leap, as graphite is a form of carbon and coal is also mostly carbon. But ORNL’s process takes impurities in coal and removes them to create material that is suitable for a battery anode.
Other methods to create synthetic graphite exist, but require more time, more cost and higher temperatures. The new process is estimated to cost 13% less than the old Acheson process, according to an analysis by ORNL researcher Prashant Nagapurkar.
In the ORNL process, if the electricity is green, the whole process is green. Especially because coal historically has this reputation as ‘dirty,’ a particularly important next step is to track emissions from the entire supply chain through the manufacturing process. This could demonstrate that it is indeed a greener option to manufacture graphite from coal.
–Prashant Nagapurkar, ORNL R&D associate
Better yet, the process doesn’t just work on coal straight out of the ground (which is where coal belongs and should stay) – it also works on coal waste like fly ash, the leftovers of previous coal mining efforts, of which there are over a hundred million tons of this hazardous waste strewn about the country. Thankfully, most of this is on the surface and won’t require further mining to get to.
Researchers say that the process could help to clean up that waste, and give it a use in powering modern vehicles. They estimate that the amount of waste in the US would be enough to provide around 30% of the graphite needed for EV batteries between now and 2050.
The process doesn’t need to be used only on coal, though. Project lead Edgar Lara-Curzio explained to Electrek how it could have potential applications on other sources of carbon:
However, while this particular project focuses on finding a positive use for coal waste, the electrochemical graphitization technology that we are scaling up can be used with other amorphous carbon sources. Once we get rid of waste coal – which would be a major environmental restoration achievement in itself – biomass (e.g., dead vegetation), petroleum, or other carbon sources could be used to manufacture graphite using the same process.
For example, methane pyrolysis, which can be used to produce hydrogen, generates solid carbon as a byproduct, which could be electrochemically graphitized for lithium-ion battery applications. This technology offers the benefit of strengthening domestic supply chains for graphite rather than relying on graphite mined and processed in foreign countries, many of which have much weaker environmental and worker protections.
The ORNL project was done in collaboration with Ramaco Carbon, a Wyoming-based company that owns multiple coal mines and provides coal for steelmaking. Ramaco says that its guiding principle is “coal is too valuable to burn.” Its focus is to find uses for coal that replace petroleum as a feedstock for various chemical and material processes at what it says will be a much lower cost.
Electrek’s Take
At first glance, this seems like some really great research. It onshores graphite supply, offers some scalable competition globally to diversify battery material sources, can be used on old waste, and is cheaper than existing processes.
But it also feels a little sketchy, because what we need to be focusing on is keeping carbon in the ground.
When we take carbon out of the ground, we sure do have a tendency to burn it, which means it ends up in the air, which is bad. Currently the air is 423ppm carbon, which is higher than the 280-350ppm range that represents a proper balance for current life on Earth. This means we don’t need to be taking carbon out of the ground, we need to be putting it back in the ground – and a lot of it.
So, any new process that might make us look at that carbon in the ground and think of another way that we might use it is suspect.
At least in this instance, it’s being proposed by a company that owns coal mines not for burning, but for finding other uses. So they might not use this as an excuse to burn more coal. Which is nice.
However, there has also been a significant push lately for coal-free steel, led by companies like SSAB in Sweden. Coal-based steelmaking (like that which Ramaco provides coal for) is linked to nearly a thousand deaths, $13 billion in healthcare costs and hundreds of thousands of lost school and work days annually in the US.
Given that this research was done in collaboration with a company that provides coal for that same dirty process, it gives us some pause. The process of turning coal into batteries will be cleaner than simply burning coal into the air, and graphite is potentially recyclable and usable long-term in multiple generations of electric car batteries, but it’s hard to shake the fact that coal is one of the most-polluting substances humans have available to us.
So, would we be giving ourselves more reasons to take coal out of the ground with this process? Even though researchers point out that coal waste can be used in this process, what if companies find out that it’s more difficult or costly to process the waste than it is to dig up new coal?
Given that we stubbornly refuse to impose the real price of this pollution on the companies that cause it, it’s entirely possible that coal mines will figure out a way to use this to justify their continued operation (especially whenever a republican administration, who have routinely shown themselves to be hostile to human health and too cozy with the coal industry, finds itself in charge).
So while new science is never a bad thing, this strikes me as something that we should keep an eye on. Cleaning up the environmental disaster of stranded coal waste is a fantastic usage, but lets not let this forestall the rapid shutting down of coal mines in this country.
Another thing you can use batteries for? Powering your home! To limit power outages and make your home more resilient, consider going solar with a battery storage system. In order to find a trusted, reliable solar installer near you that offers competitive pricing, check out EnergySage, a free service that makes it easy for you to go solar. They have hundreds of pre-vetted solar installers competing for your business, ensuring you get high quality solutions and save 20-30% compared to going it alone. Plus, it’s free to use and you won’t get sales calls until you select an installer and you share your phone number with them.
Your personalized solar quotes are easy to compare online and you’ll get access to unbiased Energy Advisers to help you every step of the way. Get started here. – ad*
